No products in the cart.
Return To ShopHDFC BANK ACCOUNT:
- NXFEE INNOVATION,
HDFC BANK, MAIN BRANCH, PONDICHERRY-605004.
INDIA,
ACC NO. 50200090465140,
IFSC CODE: HDFC0000407.
₹16,000.00 Original price was: ₹16,000.00.₹10,000.00Current price is: ₹10,000.00.
Source : Tanner EDA
From : IEEE Transaction on VLSI System, VOL. 34, NO. 1, JANUARY 2026.
Base paper abstract:
To address the data-intensive demands of modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems, computation-in-memory(CIM) based on static random-access memory (SRAM) has emerged as a promising solution by integrating computing functionality within memory arrays. However, conventional SRAM CIM architectures face two key limitations: low output resistance in single-transistor transmission paths and voltage instability on charge-sharing bitlines. These limitations collectively degrade computational accuracy to 4–5 LSB-level integral nonlinearity (INL), restricting practical deployment. This work proposes a regulated-cascode 9T SRAM cell that enhances analog computation accuracy using a high-impedance transmission path through a cascode configuration and stabilizing the discharge amount of the bitline from a single cell via active feedback regulation. Implemented in Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC) 55-nm CMOS technology, the proposed cell demonstrates 1.31 LSB INL at 400-mV bitline swing (68.4% improvement versus 4–5 LSB baselines), achieving 66.7% voltage utilization efficiency compared with the conventional 50% limit and 23.04% frequency improvement is achieved compared with the conventional architecture. It also achieves an energy efficiency of 18.47 fJ/bit and a compact area of 2.655 × 1.175 µm, while demonstrating a classification accuracy of 97.7% on the MNIST dataset. Index Terms Analog linearity enhancement, multirow readout, regulated cascode circuits, static random-access memory (SRAM)-based compute-in-memory, voltage utilization efficiency.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
Objective:
Proposed abstract:
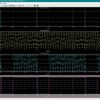
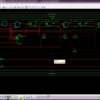
Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) plays a vital role in modern digital and embedded systems due to its high speed, simple structure, and compatibility with CMOS technology, and it is widely used in processors, biomedical devices, and real-time signal storage applications such as ECG monitoring systems. While conventional 6T SRAM offers compact area and low complexity, it suffers from read stability and delay issues at scaled technologies, whereas 8T and 9T SRAM architectures improve read reliability and performance at the cost of increased area and transistor count. In biomedical applications like ECG signal storage, where reliable and low-power digital data handling is required, selecting an optimal SRAM architecture becomes challenging. Most existing works focus either on conventional SRAM performance using generic binary inputs or on advanced compute-in-memory designs, with limited analysis on ECG-oriented digital data patterns. In this work, a comparative design and analysis of 6T, 8T, and 9T SRAM cells and their corresponding 8×8 array architectures is presented for ECG-oriented digital signal storage. Digitized ECG samples from the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database are used as realistic biomedical input stimuli, ensuring practical relevance while maintaining purely digital storage. All SRAM architectures are designed and simulated in 45 nm CMOS technology using Tanner EDA. The proposed 9T SRAM demonstrates improved delay performance and reduced power consumption compared to 6T and 8T designs, with a moderate area overhead. Performance evaluation is carried out at both single-cell and array levels under normal binary inputs and ECG-based digital stimuli, validating stable operation and consistent behaviour. The novelty of this work lies in the systematic comparison of multiple SRAM architectures under ECG-oriented digital workloads, providing design insights for low-power and reliable biomedical memory applications.
” Thanks for Visit this project Pages – Buy It Soon “
Payment Method :
HDFC BANK ACCOUNT:
₹16,000.00 Original price was: ₹16,000.00.₹10,000.00Current price is: ₹10,000.00.
₹20,000.00 Original price was: ₹20,000.00.₹10,000.00Current price is: ₹10,000.00.
Copyright © 2026 Nxfee Innovation.