Proposed Title :
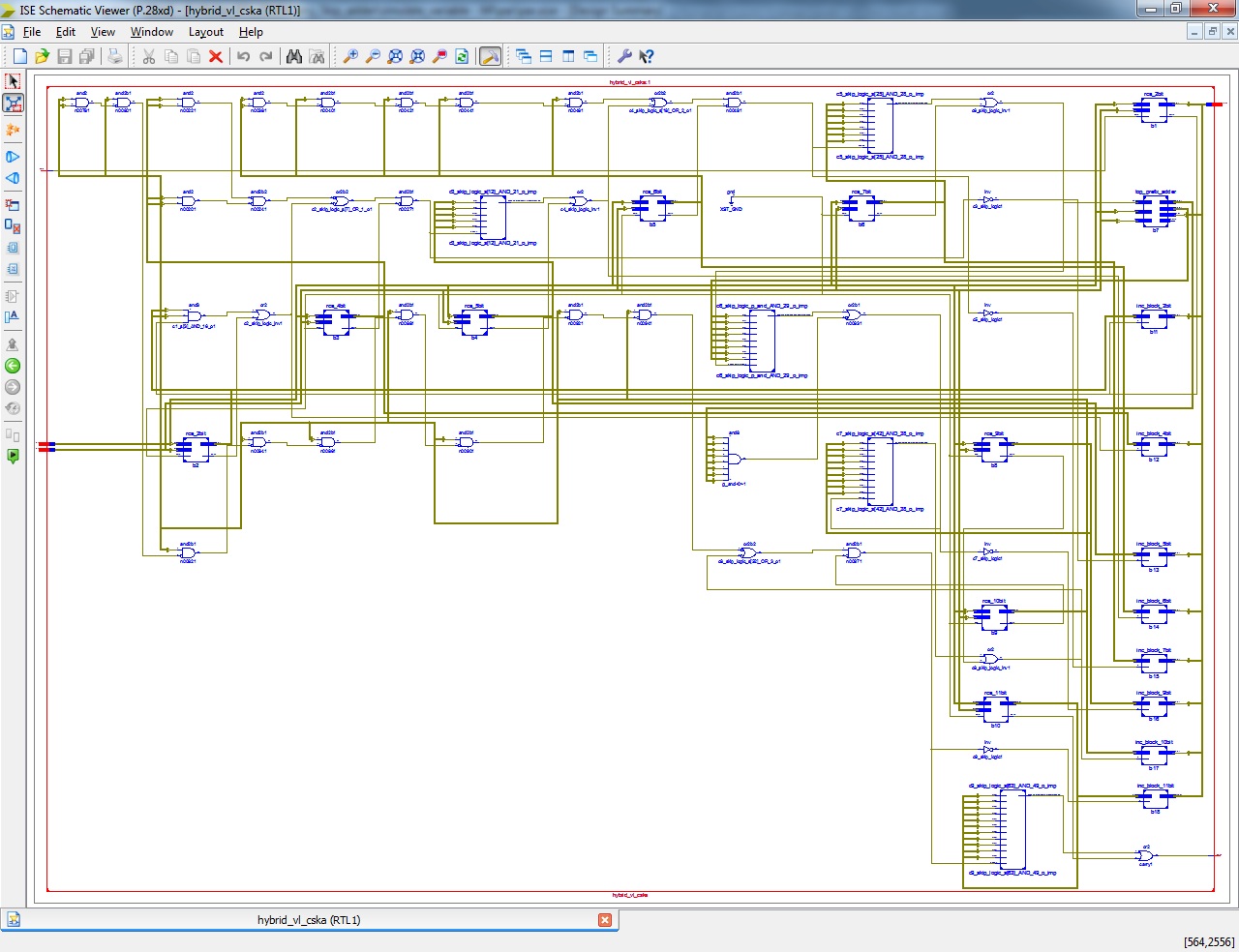
FPGA Implementation of Fixed and Variable 64 bit of High Speed Energy Efficient Carry Select Adder
Proposed System:
- To increases the bit size up to 64 bit with Fixed and Variable design of Carry Skip Adder.
Software implementation:
- Modelsim
- Xilinx

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.