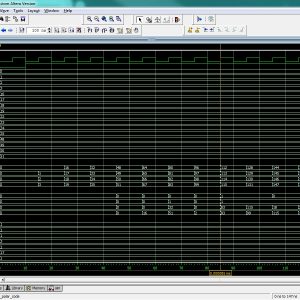
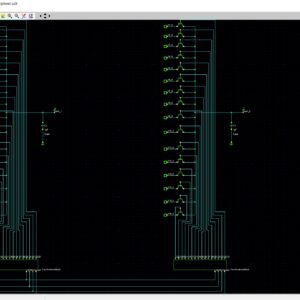
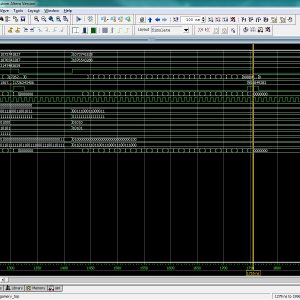
Low Power Variation Tolerant Nonvolatile Lookup Table Design
Emerging nonvolatile memories (NVMs), such as MRAM, PRAM, and RRAM, have been widely investigated to replace SRAM as the configuration bits in field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) for high security and instant power ON. However, the variations inherent in NVMs and advanced logic process bring reliability issue to FPGAs. This brief introduces a low-power variation-tolerant nonvolatile lookup table (nvLUT) circuit to overcome the reliability issue. Because of large ROFF/RON, 1T1R RRAM cell provides sufficient sense margin as a configuration bit and a reference resistor. A single-stage sense amplifier with voltage clamp is employed to reduce the power and area without impairing the reliability. Matched reference path is proposed to reduce the parasitic RC mismatch for reliable sensing. Evaluation shows that 22% reduction in delay, 38% reduction in power, and the tolerance of variations of 2.5× typical RON or ROFF in reliability are achieved for proposed nvLUT with six inputs. The proposed architecture of this paper area and power consumption analysis using tanner tool.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
A 0.1–3.5-GHz Duty-Cycle Measurement and Correction Technique in 130-nm CMOS
A duty-cycle correction technique using a novel pulse width modification cell is demonstrated across a frequency range of 100 MHz–3.5 GHz. The technique works at frequencies where most digital techniques implemented in the same technology node fail. An alternative method of making time domain measurements such as duty cycle and rise/fall times from the frequency domain data is introduced. The data are obtained from the equipment that has significantly lower bandwidth than required for measurements in the time domain. An algorithm for the same has been developed and experimentally verified. The correction circuit is implemented in a 0.13-µm CMOS technology and occupies an area of 0.011 mm2. It corrects to a residual error of less than 1%. The extent of correction is limited by the technology at higher frequencies. The proposed architecture of this paper area and power consumption analysis using tanner tool.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
OTA-Based Logarithmic Circuit for Arbitrary Input Signal and Its Application
In this paper, a new design procedure has been proposed for realization of logarithmic function via three phases: 1) differentiation; 2) division; and 3) integration for any arbitrary analog signal. All the basic building blocks, i.e., differentiator, divider, and integrator, are realized by operational transconductance amplifier, a current mode device. Realization of exponential, power law and hyperbolic function as the design examples claims that the proposed synthesis procedure has the potential to design a log-based nonlinear system in a systematic and hierarchical manner. The proposed architecture of this paper area and power consumption analysis using tanner tool.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:A High-Throughput VLSI Architecture for Hard and Soft SC-FDMA MIMO Detectors
Abstract:
A novel low-complexity multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) detector tailored for single-carrier frequency division-multiple access (SC-FDMA) systems, suitable for efficient hardware implementations. The proposed detector starts with an initial estimate of the transmitted signal based on a minimum mean square error (MMSE) detector. Subsequently, it recognizes less reliable symbols for which more candidates in the constellation are browsed to improve the initial estimate. The proposed architecture of this paper analysis the logic size, area and power consumption using Xilinx 14.2.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:To develop and Implement Low Power, High Speed VLSI for Processing Signals using Multi rate Techniques Low Power Divider Using Vedic Mathematics
Abstract:
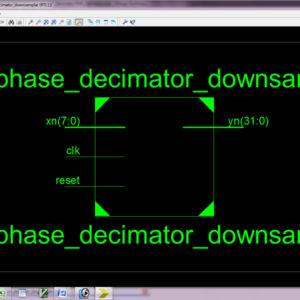
Multirate technique is necessary for systems with different input and output sampling rates. Recent advances in mobile computing and communication applications demand low power and high speed VLSI DSP systems. In this paper to discuss the downsampling technique and its improvement, major drawbacks of present approaches possible to increase degeneracy. This Multirate design methodology is systematic and applicable to many problems. The proposed architecture of this paper analysis the logic size, area and power consumption using Xilinx 14.2.The proposed architecture of this paper analysis the logic size, area and power consumption using Xilinx 14.2.
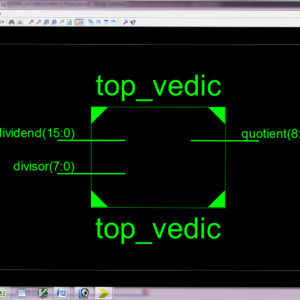
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:Low Power Divider Using Vedic Mathematics
Vedic mathematics is a unique technique of carrying out mathematical computations and it has its roots in the ancient Indian Mathematics. This paper presents the divider architecture using one of the Vedic mathematics techniques called as Paravartya-Yojayet, which means to transpose and apply. This paper proposes a fast, low power and cost effective architecture of a divider using the ancient Indian Vedic division algorithm. The merits of the proposed architecture are proved by comparing the gate count, power consumption and delay against the conventional divider architectures. The proposed architecture of this paper analysis the logic size, area and power consumption using Xilinx 14.2.
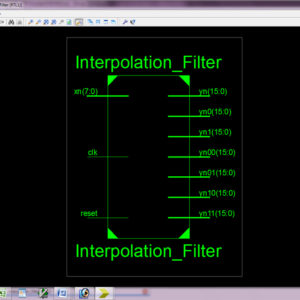
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:Novel Block-Formulation and Area-Delay-Efficient Reconfigurable Interpolation Filter Architecture for Multi-Standard SDR Applications
Abstract: The input-matrix and the coefficient-matrix resizes when changes. An analysis of interpolation filter computation for different up-sampling factors is made in this paper to identify redundant computations and removed those by reusing partial results. Reuse of partial results eliminates the necessity of matrix resizing in interpolation filter computation. A novel block-formulation is presented to share the partial results for parallel computation of filter outputs of different up-sampling factors. Using the proposed block formulation, to increase the number of tab to 16 and to get the accuracy and reduce the delay. The proposed architecture of this paper analysis the logic size, area and power consumption using Xilinx 14.2.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
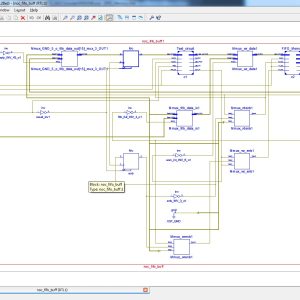
In-Field Test for Permanent Faults in FIFO Buffers of NoC Routers
Abstract:
This brief proposes an on-line transparent test technique for detection of latent hard faults which develop in first input first output buffers of routers during field operation of NoC. The technique involves repeating tests periodically to prevent accumulation of faults. A prototype implementation of the proposed test algorithm has been integrated into the router-channel interface and on-line test has been performed with synthetic self-similar data traffic. The performance of the NoC after addition of the test circuit has been investigated in terms of throughput while the area overhead has been studied by synthesizing the test hardware. In addition, an on-line test technique for the routing logic has been proposed which considers utilizing the header flits of the data traffic movement in transporting the test patterns.
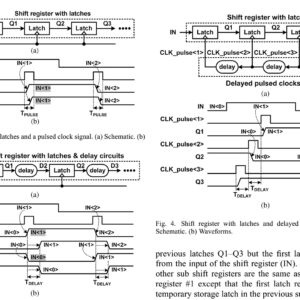
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:Low Power and Area Efficient Shift Register Using Pulsed Latches
Abstract: This paper proposes a low-power and area-efficient shift register using pulsed latches. The area and power consumption are reduced by replacing flip-flops with pulsed latches. This method solves the timing problem between pulsed latches through the use of multiple non-overlap delayed pulsed clock signals instead of the conventional single pulsed clock signal. The shift register uses a small number of the pulsed clock signals by grouping the latches to several sub shifter registers and using additional temporary storage latches. The proposed architecture of this paper analysis the area and power using tanner tool.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:Design and Low-Complexity Implementation of Matrix–Vector Multiplier for Iterative Methods in Communication Systems
Abstract: Iterative methods are basic building blocks of communication systems and often represent a dominating part of the system, and therefore, they necessitate careful design and implementation for optimal performance. In this brief, we propose a novel field programmable gate arrays design of matrix–vector multiplier that can be used to efficiently implement widely adopted iterative methods. The proposed design exploits the sparse structure of the matrix as well as the fact that spreading code matrices have equal magnitude entries. Implementation details and timing analysis results are promising and are shown to satisfy most modern communication system requirements.
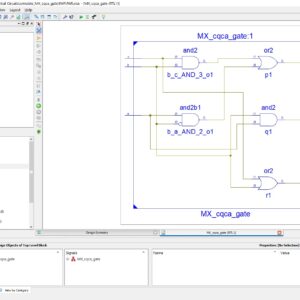
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:Design of Testable Reversible Sequential Circuits
Abstract: In this paper, we propose the design of two vectors testable sequential circuits based on conservative logic gates. The proposed sequential circuits based on conservative logic gates outperform the sequential circuits implemented in classical gates in terms of testability. Any sequential circuit based on conservative logic gates can be tested for classical unidirectional stuck-at faults using only two test vectors. The two test vectors are all 1s, and all 0s. The designs of two vectors testable latches, master-slave flip-flops and double edge triggered (DET) flip-flops are presented. The importance of the proposed work lies in the fact that it provides the design of reversible sequential circuits completely testable for any stuck-at fault by only two test vectors, thereby eliminating the need for any type of scan-path access to internal memory cells. The reversible design of the DET flip-flop is proposed for the first time in the literature. We also showed the application of the proposed approach toward 100% fault coverage for single missing/additional cell defect in the quantum dot cellular automata (QCA) layout of the Fredkin gate. We are also presenting a new conservative logic gate called multiplexer conservative QCA gate (MX-cqca) that is not reversible in nature but has similar properties as the Fredkin gate of working as 2:1 multiplexer. The proposed MX-cqca gate surpasses the Fredkin gate in terms of complexity (the number of majority voters), speed, and area.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:Reverse Converter Design via Parallel-Prefix Adders: Novel Components, Methodology, and Implementations
Abstract: The implementation of residue number system reverse converters based on well-known regular and modular parallel prefix adders is analyzed. The VLSI implementation results show a significant delay reduction and area × time2 improvements, all this at the cost of higher power consumption, which is the main reason preventing the use of parallel-prefix adders to achieve high-speed reverse converters in nowadays systems. Hence, to solve the high power consumption problem, novel specific hybrid parallel-prefix-based adder components those provide better tradeoff between delay and power consumption. The power, area and delay of the proposed system are analysis using Xilinx 14.2.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:FPGA Implementation of Partially Parallel Encoder Architecture for Long Polar Code
Polar coding is an encoding/decoding scheme that provably achieves the capacity of the class of symmetric binary memory-less channels. Due to the channel achieving property, the polar code has become one of the most favourable error-correcting codes. As the polar code achieves the property asymptotically, however, it should be long enough to have a good error-correcting performance. Although previous fully parallel encoder is intuitive and easy to implement, it is not suitable for long polar codes because of the huge hardware complexity required. In the brief, we analyse the encoding process in the viewpoint of very large-scale integration implementation and propose a new efficient encoder architecture that is adequate for long polar codes and effect in alleviating the hardware complexity. As the proposed encoder allows high-throughput encoding with small hardware complexity, it can be systematically applied to the design of any polar code and to any level of parallelism. Finally shown the power, area, delay report with comparison of existing work.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
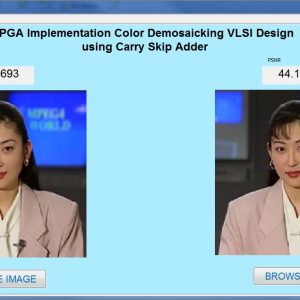
Fully Pipelined Low-Cost and High-Quality Color Demosaicking VLSI Design for Real-Time Video Applications
This system presents a fully pipelined color demosaicking design. To improve the quality of reconstructed images, a linear deviation compensation scheme was created to increase the correlation between the interpolated and neighboring pixels. Furthermore, immediately interpolated green color pixels are first to be used in hardware-oriented color demosaicking algorithms, which efficiently promoted the quality of the reconstructed image. A boundary detector and boundary mirror machine were added to improve the quality of pixels located in boundaries. In addition, a hardware sharing technique was used to reduce the hardware costs of three interpolators. Finally these are implemented and get the simulated result is compared to the previous architecture. The code are simulated and power, area, cost are taken using Xilinx 14.2 software and MATLAB. Compared with the previous low complexity designs, this work has the benefits in terms of low cost, low power consumption, and high performance.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
Quaternary Logic Lookup Table in Standard CMOS
Abstract: Interconnections are increasingly the dominant contributor to delay, area and energy consumption in CMOS digital circuits. The proposed implementation overcomes several limitations found in previous quaternary implementations published so far, such as the need for special features in the CMOS process or power-hungry current-mode cells. We have to use the 512bit quaternary Look Up Table for high level of operations in the FPGA. The proposed architecture of this paper will be planned to implemented and also analysis the output current, output voltage, area using Xilinx 14.3.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:Low-Cost High-Performance VLSI Architecture for Montgomery Modular Multiplication
Source Code : VHDL & VERILOG HDL
Abstract: This paper proposes a simple and efficient Montgomery multiplication algorithm such that the low-costand high-performance Montgomery modular multiplier can be implemented accordingly. The proposed multiplier output data with representation and uses only one parallel prefix adder to avoid a carry propagation and reduce the area, power and delay, and also increasing the speed. Mainly the usage of parallel prefix adder is to reduce the significant delay reduction and area × time2 improvements, all this at the cost of higher power consumption, which is the main reason preventing the use of parallel-prefix adders to achieve high-speed reverse converters in nowadays systems. Hence, to solve the high power consumption problem, novel specific hybrid parallel-prefix-based adder components those provide better trade-off between delay and power consumption. As a result, the extra clock cycles for operand pre-computation and format conversion can be hidden and high throughput can be obtained. Experimental results show that the proposed Montgomery modular multiplier can achieve higher performance and significant area–time product improvement when compared with previous designs. Using VHDL to design the RTL, and the result to be shown in Xilinx 14.2 with Power consumption and area reduction.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
Byte-Reconfigurable LDPC Codec Design With Application to High-Performance ECC of NAND Flash Memory Systems
Abstract: In information theory, a low-density parity-check (LDPC) code is a linear error correcting code, a method of transmitting a message over a noisy transmission channel. An LDPC is constructed using a sparse bipartite graph. LDPC codes are capacity-approaching codes, which means that practical constructions exist that allow the noise threshold to be set very close (or even arbitrarily close on the BEC) to the theoretical maximum (the Shannon limit) for a symmetric memory-less channel. The noise threshold defines an upper bound for the channel noise, up to which the probability of lost information can be made as small as desired. Using iterative belief propagation techniques, LDPC codes can be decoded in time linear to their block length.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:An Efficient Constant Multiplier Architecture Based on Vertical-Horizontal Binary Common Sub-expression Elimination Algorithm for Reconfigurable FIR Filter Synthesis.
Abstract: This paper proposes efficient constant multiplier architecture based on vertical-horizontal binary common sub-expression elimination (VHBCSE) algorithm for designing a reconfigurable finite impulse response (FIR) filter whose coefficients can dynamically change in real time. To design an efficient reconfigurable FIR filter, according to the proposed VHBCSE algorithm, 2-bit binary common sub-expression elimination (BCSE) algorithm has been applied vertically across adjacent coefficients on the 2-D space of the coefficient matrix initially, followed by applying variable-bit BCSE algorithm horizontally within each coefficient. Faithfully rounded truncated multiple constant multiplication/accumulation (MCMAT) and multi-root binary partition graph (MBPG) respectively. Efficiency shown by the results of comparing the FPGA and ASIC implementations of the reconfigurable FIR filter designed using VHBCSE algorithm based constant multiplier establishes the suitability of the proposed algorithm for efficient fixed point reconfigurable FIR filter synthesis.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:Algorithm and Architecture for a Low Power Content Addressable Memory Based on Sparse Clustered Networks
Abstract: We propose a low-power content-addressable memory (CAM) employing a new algorithm for associativity between the input tag and the corresponding address of the output data of 128bit. The proposed architecture is based on a recently developed sparse clustered network using binary connections that on-average eliminates most of the parallel comparisons performed during a search. Therefore, the dynamic energy consumption of the proposed design is significantly lower compared with that of a conventional low-power CAM design. Given an input tag, the proposed architecture computes a few possibilities for the location of the matched tag and performs the comparisons on them to locate a single valid match. A design methodology based on the silicon area and power budgets, and performance requirements is discussed. The proposed architecture of this paper will be analysis the logic size, area and power consumption using Xilinx 14.2.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
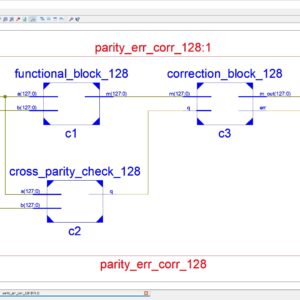
A Low-Complexity Multiple Error Correcting Architecture Using Novel Cross Parity Codes Over GF(2 m)
Abstract: This paper presents a modern low- complexity cross parity code, with a wide range of multiple bit error correction capability at a lower overhead, for improving the reliability. We have to use the two type of error correction technique for 128bit; first one is single bit error correction by using the hamming code. This hamming code is detects and then correct the single bit error correction. Another one is multiple bits error correction by using BCH (Bose–Choudhury– Hocquenghem). This one corrects the multiple bits error. Finally these are implemented and get the simulated result is compared to the previous architecture. The code are simulated and power, area, cost are taken using Xilinx 14.2 software.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
Modified Wallace Tree Multiplier using Efficient Square Root Carry Select Adder
A multiplier is one of the key hardware blocks in most digital and high performance systems such as FIR filters, micro processors and digital signal processors etc. A system’s performance is generally determined by the performance of the multiplier because the multiplier is generally the slowest element in the whole system and also it is occupying more area consuming. The Carry Select Adder (CSLA) provides a good compromise between cost and performance in carry propagation adder design. A Square Root Carry Select Adder using RCA is introduced but it offers some speed penalty. However, conventional CSLA is still area-consuming due to the dual ripple carry adder structure. In the proposed work, generally in Wallace multiplier the partial products are reduced as soon as possible and the final carry propagation path carry select adder is used. In this paper, modification is done at gate level to reduce area and power consumption. The Modified Square Root Carry Select-Adder (MCSLA) is designed using Common Boolean Logic and then compared with regular CSLA respective architectures, and this MCSLA is implemented in Wallace Tree Multiplier. This work gives the reduced area compared to normal Wallace tree multiplier. Finally an area efficient Wallace tree multiplier is designed using common Boolean logic based square root carry select adder.
List of the following materials will be included with the Downloaded Backup:
Provide Wordlwide Online Support
We can provide Online Support Wordlwide, with proper execution, explanation and additionally provide explanation video file for execution and explanations.
24/7 Support Center
NXFEE, will Provide on 24x7 Online Support, You can call or text at +91 9789443203, or email us nxfee.innovation@gmail.com
Terms & Conditions:
Customer are advice to watch the project video file output, and before the payment to test the requirement, correction will be applicable.
After payment, if any correction in the Project is accepted, but requirement changes is applicable with updated charges based upon the requirement.
After payment the student having doubts, correction, software error, hardware errors, coding doubts are accepted.
Online support will not be given more than 3 times.
On first time explanation we can provide completely with video file support, other 2 we can provide doubt clarifications only.
If any Issue on Software license / System Error we can support and rectify that within end of day.
Extra Charges For duplicate bill copy. Bill must be paid in full, No part payment will be accepted.
After payment, to must send the payment receipt to our email id.
Powered by NXFEE INNOVATION, Pondicherry.
Call us today at : +91 9789443203 or Email us at nxfee.innovation@gmail.com
NXFEE Development & Services

Copyright © 2026 Nxfee Innovation.